How Does Business Internet Differ From Residential Plans: Key Factors You Should Know
By PAGE Editor
Choosing between business and residential internet affects how smoothly your workday runs and how reliably you stay connected. The difference goes beyond price—every aspect, from performance to support, changes depending on your needs. Business internet provides faster speeds, stronger reliability, and professional-grade support with features designed to keep operations running without interruption.
You use residential internet for everyday activities like streaming or browsing, but when you rely on stable uploads, video calls, or shared file access, business internet becomes essential. Service level agreements, dedicated bandwidth, and static IP options help protect uptime and security, giving you consistent performance that household plans can’t guarantee.
Key Takeaways
Business internet delivers higher reliability and better performance for professional use.
Residential internet offers affordability and features tailored for personal use.
Advanced business features provide stronger security and support for continuous operations.
Key Differences Between Business and Residential Internet Plans
Business and residential internet plans use similar technologies but serve different purposes. You can expect distinctions in network speed, reliability, service agreements, and pricing that directly affect how well each plan fits your needs.
Speed and Bandwidth
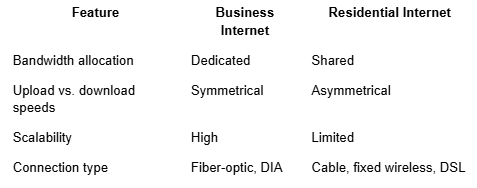
Business internet plans focus on consistent and scalable bandwidth. They often use dedicated connections like fiber-optic or direct internet access (DIA), providing symmetrical speeds for uploads and downloads. This design supports data-heavy operations such as video conferencing, file transfers, and cloud applications.
Residential internet, often delivered through shared bandwidth, prioritizes download speeds over uploads since most home users stream or browse more than they send data. For example, a residential internet plan might offer 500 Mbps download and only 25 Mbps upload.
Many business internet providers guarantee speed consistency throughout the day, even during high-traffic periods. This ensures stable performance for multiple users and devices. Residential internet can slow down when neighborhood demand spikes because the connection is shared among many households.
Reliability and Uptime Guarantees
Reliability is critical for operations that depend on continuous internet connectivity. Business internet plans usually come with uptime guarantees—often 99.9% or higher—backed by measurable performance commitments. These guarantees minimize the risk of lost productivity due to downtime.
Residential internet plans rarely include such guarantees. While they can deliver high-speed internet, unexpected outages or network slowdowns may happen without compensation or priority repair.
You can expect network reliability from business-grade services because internet service providers (ISPs) prioritize essential traffic and use redundant infrastructure. Fiber-optic connections, for instance, reduce latency and improve stability. Residential internet, by contrast, relies on broader shared networks that are more vulnerable to interruptions.
For mission-critical operations, such as e-commerce platforms or remote desktop access, even brief downtime can have significant impacts. A business connection provides the reliability necessary to maintain performance when your customers or employees depend on real-time access.
Service Level Agreements and Customer Support
A cornerstone of business internet is the Service Level Agreement (SLA). SLAs define performance standards such as uptime, latency, and response time for outages. They also outline compensation if the provider fails to meet those metrics. This formal accountability ensures predictable service quality.
Residential customers typically rely on best-effort support without guaranteed response times. Outage tickets may take longer to resolve, and tech support often follows standard business hours.
Businesses receive priority customer service and access to dedicated technical support teams that operate 24/7. For instance, if your office experiences network downtime, your ISP can dispatch a technician or provide remote recovery within hours. This level of service helps prevent prolonged disruptions.
When evaluating providers, review their SLA terms in detail. Well-established networks, such as business internet from Digicel , specify their performance commitments clearly, giving you confidence that service quality aligns with your operational demands.
Cost Considerations and Value
You will notice that business internet plans cost more than residential ones. The higher price reflects the additional resources behind dedicated bandwidth, enhanced customer support, and SLA-backed reliability.
Typical residential internet plans are designed for streaming, gaming, and basic browsing, offering affordability and sufficient capacity for household needs. Business users, however, often require scalable bandwidth and redundant infrastructure to handle heavy data transfers or multiple VPN sessions.
While the upfront expense is higher, business-grade internet provides measurable value. Reliable connectivity reduces the risk of lost revenue from downtime, and faster uploads improve workflow efficiency.
When comparing internet costs, consider the total cost of ownership, not just the monthly fee. Savings from improved productivity and fewer outages can offset the apparent cost differences between business and residential internet services.
Advanced Features and Security Considerations
Business internet emphasizes stability, data protection, and control over network resources. It supports advanced features that let you securely manage sensitive information, maintain consistent performance, and expand connectivity as your operations grow.
Static Versus Dynamic IP Addresses
A major distinction between business and residential internet lies in IP address assignment. Most residential connections use dynamic IP addresses, which automatically change over time. This setup requires less configuration but can disrupt remote access tools or hosted services.
Business connections often include one or more static IP addresses, which remain fixed. Static IPs simplify hosting web servers, VPN access, and point-of-sale systems, as external users or devices can reliably connect to the same address.
Some providers offer blocks of static IPs for companies that manage multiple users or remote offices. These addresses also support cloud computing and network monitoring solutions that depend on stable endpoints. Although static IPs increase exposure to cyber threats, maintaining strong firewalls and regular device updates can reduce risks.
Enhanced Security and Network Protection
Business internet typically includes stronger network security measures than residential service. Providers may integrate firewalls, DDoS protection, and advanced cybersecurity monitoring at the network level. These features help prevent downtime that could disrupt e-commerce operations or cloud-based workflows.
You can often customize security protocols, enabling VPN connections and secure remote access for employees. Dedicated IP configurations and prioritized bandwidth also reduce vulnerabilities from shared networks.
Residential services usually rely on consumer-grade routers, which offer only basic protections. With business internet, you gain access to managed security options, traffic filtering, and intrusion detection systems. These tools help maintain compliance and data integrity across your WAN and local networks.
Scalability and Customization Options
Business internet is built for scalability as your operations expand. It supports higher speeds, multiple users, and added features like dedicated bandwidth or internet backup plans that maintain uptime during outages.
You can adjust service tiers to match growth in cloud computing, remote collaboration, and data usage. Providers often allow you to prioritize applications such as video conferencing or point-of-sale systems through managed quality-of-service settings.
Residential plans rarely include this level of flexibility. In contrast, business services let you customize configurations for branch connectivity or private links between offices. This scalability ensures reliable performance and gives you the control needed to maintain consistent network quality as your business environment changes.
Conclusion
You’ve seen that business internet focuses on reliability, dedicated support, and symmetrical speeds that handle tasks like cloud backups or video conferencing. Residential plans, by contrast, prioritize affordability and download performance for everyday use.
Your choice depends on how much connectivity impacts your work. If you rely on consistent uptime and quick issue resolution, the higher cost of a business plan may be justified. For casual browsing or streaming, a residential plan usually meets your needs.
Carefully evaluating these differences helps you select the plan that best supports your goals and daily requirements.
HOW DO YOU FEEL ABOUT FASHION?
COMMENT OR TAKE OUR PAGE READER SURVEY
Featured









People sometimes arrive for their first appointment with hope and apprehension.